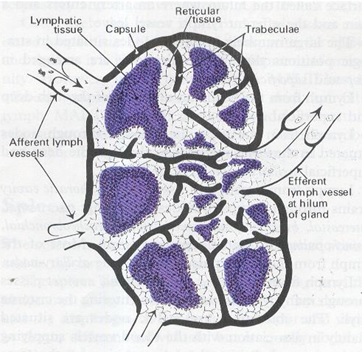
The Lymphnode
Short note on lymph node
Lymph nodes are collections of lymphoid tissue at strategic points
Small and medium sized lymph vessels open into lmph nodes
The lymph runs through 8 – 10 nodes before reaching the blood stream
Structure
Capsule – fibrous tissue – forms trabeculae (partitions)
Substance of the lymph node is made of lymphatic tissue
Contains lymphocytes and macrophages
4 – 5 afferent lymph vessels enter the lymph node
One efferent lymph vessel carries lymph away from the node
Lymph node – has a hilum – through which an artery enters and a vein and efferent lymph vessel leave
Situation
Lymph nodes – deep and superficial groups
For head & neck – deep and superficial cervical nodes
Upper limbs – nodes in the elbow regions – deep and superficial axillary nodes
Lower limbs – deep and superficial nodes including popliteal nodes and inguinal nodes
Breast – axillary nodes
Thoracic cavity – parasternal, intercostal, brachiocepalic, mediastinal, tracheobronchial, bronchopulmonary and eosophageal nodes
Pelvic and abdominal cavities – nodes associated with the blood vessels supplying the organs and close to the main arteries i.e. The aorta and external and internal iliac arteries.
Functions of Lymph Nodes
Filtering and phagocytosis
Proliferation of lymphocytes
Activated T and B lymphocytes multiply in lymph nodes
Antibodies produced by sensitised B-lymphocytes enter lymph and blood from the node